Windows
Server 2008
Windows Server 2008 is one of Microsoft Windows' server lines of operating systems. Its officially released on February 27, 2008, it is the successor to Windows Server 2003, released nearly five years earlier. A second release, named Windows Server 2008 R2, was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009. Like Windows Vista and Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 is based on Windows NT 6.x. window server 2008 is the most advanced windows yet designed to power the next generation of network
System Hardware Requirements of Window Server 2008
2. Select the language Than Click on Next.
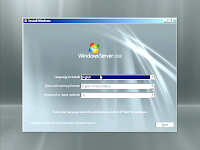
3. Click on Install Now.
4. Enter the 25 character Product Key
5. Click [YES] if you inserted the product key if you not inserted 25 character
Product key select [NO] Click on Next.
6. Select your window server 2008 product version and check Box at the bottom of the screen
☑. I have selected the edition of window that I purchased.
7. Accept the license click on next.
8. Click to Custom Installation.
9. Now need to create a Hard Disk Drive Partition: Click on next.
10. Select a partition where you want to install window server 2008
11. Click on next.
12. After clicking next this session will start the installing process.
13. After completing installation process system will automatically reboot.
14. After rebooting you should see similar to the following screen here you need to
click on [ok]
15. Give Administrator Password Two times than click arrow Mark.
16. Password changed successfully and now you can login now.
2. Double Click On Roles.
3. Click on ADD Roles.
4. Click on next Bypass welcome screen
5. Now you will see the select roles screen
6. ☑Checkmark the Box if you want to install any server Roles.
7. Click Next to continue.
8. Click Install to being Installation
9. After Few mints Installation will complete now you can start the using your server 2008 .

Windows Server 2008 is one of Microsoft Windows' server lines of operating systems. Its officially released on February 27, 2008, it is the successor to Windows Server 2003, released nearly five years earlier. A second release, named Windows Server 2008 R2, was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009. Like Windows Vista and Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 is based on Windows NT 6.x. window server 2008 is the most advanced windows yet designed to power the next generation of network
System Hardware Requirements of Window Server 2008
Component
|
Requirement
|
Processor
|
Minimum: 1 GHz (x86 processor) or 1.4 GHz
(x64 processor)
|
Memory
|
Minimum: 512 MB RAM
|
Available Disk Space
|
Minimum: 10 GB
|
Drive
|
DVD-ROM drive
|
Peripherals
|
Keyboard/Mouse
|
Step By Step
Installation server 2008
1.
Insert the window server 2008 DVD into DVD ROM of Computer.2. Select the language Than Click on Next.

3. Click on Install Now.
4. Enter the 25 character Product Key
5. Click [YES] if you inserted the product key if you not inserted 25 character
Product key select [NO] Click on Next.
6. Select your window server 2008 product version and check Box at the bottom of the screen
☑. I have selected the edition of window that I purchased.
7. Accept the license click on next.
8. Click to Custom Installation.
9. Now need to create a Hard Disk Drive Partition: Click on next.
10. Select a partition where you want to install window server 2008
11. Click on next.
12. After clicking next this session will start the installing process.
13. After completing installation process system will automatically reboot.
14. After rebooting you should see similar to the following screen here you need to
click on [ok]
15. Give Administrator Password Two times than click arrow Mark.
16. Password changed successfully and now you can login now.
Configure
Server Roles on Window Server 2008
1.
Click On Start -> Programs -> Administrator Tools-> Select server
Manager2. Double Click On Roles.
3. Click on ADD Roles.
4. Click on next Bypass welcome screen
5. Now you will see the select roles screen
6. ☑Checkmark the Box if you want to install any server Roles.
7. Click Next to continue.
8. Click Install to being Installation
9. After Few mints Installation will complete now you can start the using your server 2008 .


